Metacognition therapy worksheet
Download Worksheet
What is the theory behind this Metacognition therapy worksheet?
This worksheet is based on a self regulatory executive function model, according to which people with emotional issues develop a certain pattern of thinking known as the Cognitive Attentional Syndrome (CAS). This thinking pattern is a result of one’s positive or negative metacognition beliefs i.e beliefs about one’s thinking.
People with CAS tend to cope with emotional distress through thinking strategies that they believe are helpful when they actually aren’t. These include worry, rumination, threat monitoring, thought control strategies, avoidance, and reassurance seeking. Treatment is meant to target the way they think about their ‘thinking’ and modify it to be helpful.
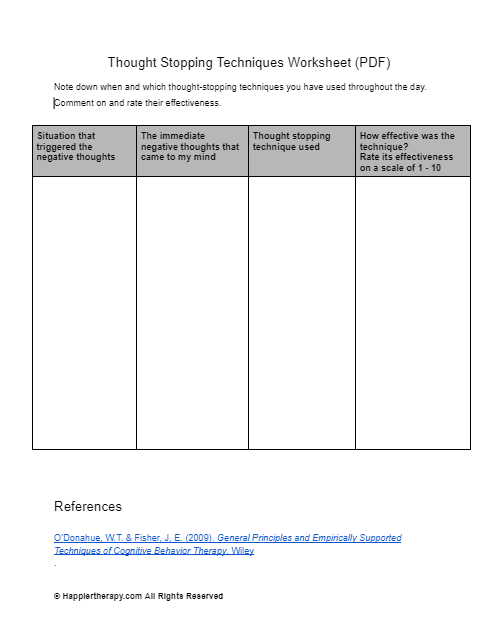
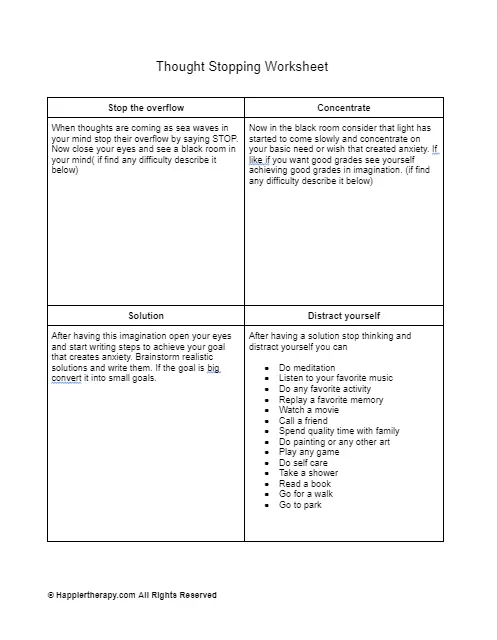
How will the worksheet help?
The worksheet will help clients who have a habit of worrying excessively. Instead of addressing the cause of their worry they focus on the content of the worry giving it the power to cause significant distress. This exercise will help them identify and challenge their beliefs about worry.
How to use the worksheet?
The worksheet can be used in session during discussion about positive and negative beliefs about worry that the client has. The therapist can explain the vicious cycle that develops as a result of it. In the second part, instruct the client to practice writing down their worries about a situation and then giving it a reality check.

 By
By